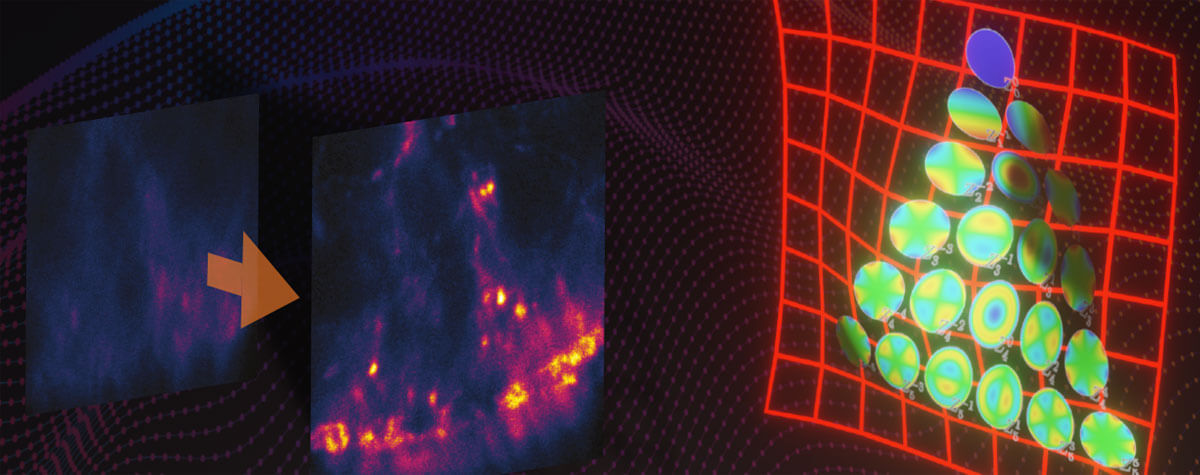
Confocal and multi-photon microscopy are used for deep tissue imaging, but misconceptions about their utility have led to their misuse. We’ll plunge into tissue depths to reveal a gap in obtaining sharp images that RAYSHAPE – a solution for dynamic aberration correction – fills with clarity and brightness. Details >
Knowledge Base
Have you ever wondered how superresolution microscopy works? What’s the difference between STED, STORM, and MINFLUX? What is “resolution” and what is a “PSF”? What is so special about the STEDYCON? Read on to find out.
If you have any suggestions, questions or ideas for our knowledge base, we would be very happy to hear from you.
ContactEverything about light microscopes, dyes, and imaging
How does STED work?

You have heard of STED but don’t have a clear idea how it overcomes the diffraction-limited resolution of confocal microscopes? You maybe even think it to be somewhat complicated? In fact, it isn’t. It’s just physics, smartly applied. Details >
Since the 1990s, confocal microscopes have been a staple in labs visualizing biological or material specimens. The development of STED microscopy prompted the question: how does the established confocal microscope compare to the (now not so) “new kid on the block”? Details >
Every technique that allows to observe cells is more or less invasive and fluorescence microscopy is no exception. Many imaging situations profit from a reduction in light dose as provided by FLEXPOSURE adaptive illumination. Details >
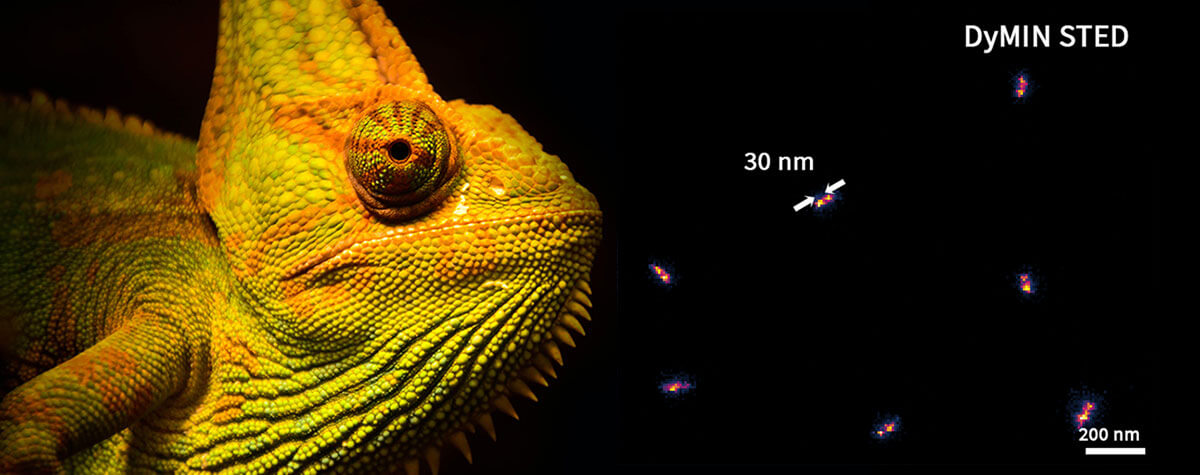
MATRIX STED is the next level of STED microscopy – combining superior resolution with outstanding signal quality and clarity. Details >
Ideal imaging conditions are often compromised by imperfections in the optical path. These can severely compromise a microscope’s performance, unless they are eliminated by RAYSHAPE's deformable mirror. Details >