NHS ester protocol
Dyes with an N-hydroxysuccinimidyl (NHS) ester are amino-reactive derivatives and are most commonly used to label proteins such as antibodies. This reactive group helps to form a chemically stable bond between the dye and the protein (antibody).
for the easy and proper application of abberior NHS labels
Introduction
abberior offers a variety of excellent fluorescent dyes with properties optimized for the labeling of biomolecules, spectroscopic studies, and optical microscopy, particularly super-resolution microscopy, and optical nanoscopy.
Dyes with an N-hydroxysuccinimidyl (NHS) ester are amino-reactive derivatives and are most commonly used to label proteins such as antibodies. This reactive group helps to form a chemically stable bond between the dye and the protein (antibody). Because of stability reasons some of our dyes are not offered as NHS ester but as NHS carbonate. For both derivatives the labeling procedure is equal. For the following protocol, the term NHS refers to both, NHS ester and NHS carbonate.
Storage
The product contains a vial of dried, solid substance and is shipped at room temperature. Upon arrival, the product can be stored at –20 °C to –80 °C for long-term storage of up to one year. The conjugate should be protected from direct light exposure and repeated freeze-thaw cycles should be avoided.
Note: Depending on solvent quality the shelf-life of the NHS solution might be significantly reduced compared to the NHS in its solid form – even if stored at –20 °C.
Antibody labeling with abberior NHS
The procedure below has been successfully tested with our abberior dyes. This procedure has yielded consistent results in most instances but may require further optimization for particular proteins or a specific degree of labeling (DOL). The following protocol describes the labeling procedure for secondary IgG antibodies.
Required reagents, not provided
- Proteins such as Antibodies (without BSA or sodium azide)
- 1x Phosphate-buffered saline pH 7.4 (PBS)
- Amino- and water-free DMF or DMSO
- NaHCO3 (pH~8.3-8.5)
- Gel filtration column (Sephadex G25, PD-10 desalting columns)
- Assay and/or device to determine protein concentration (e.g. Bradford assay, Nanodrop)
Labeling procedure
All steps are carried out at room temperature unless stated otherwise.
- Add 250 µl of 1 M aq. NaHCO3 to the antibody solution to provide a pH value between 8.0 to 8.5.
Note: The antibody solution must be BSA-free.
- Fill up the antibody solution with PBS to reach a final volume of 2500 µl.
- Dissolve the NHS-dye derivative in fresh anhydrous DMF or DMSO (10 mg/ml).
- Add 50 to 100 µg of the dye-NHS derivative per 1 mg antibody into the antibody solution.
- Gently stir the reaction mixture at room temperature for 1 h and in the dark.
- Meanwhile, prepare the gel filtration column as specified by the manufacturer.
- Transfer the antibody-dye reaction mixture onto the gel filtration column and run the solution through the column until there is no liquid standing on the column. Then elute the dye-labeled antibodies from the column with a sufficient amount of PBS buffer (approx. 3.0 to 3.5 ml).
- During elution, fractionate the liquid dripping from the column into tubes (e.g. 0.5 ml each).
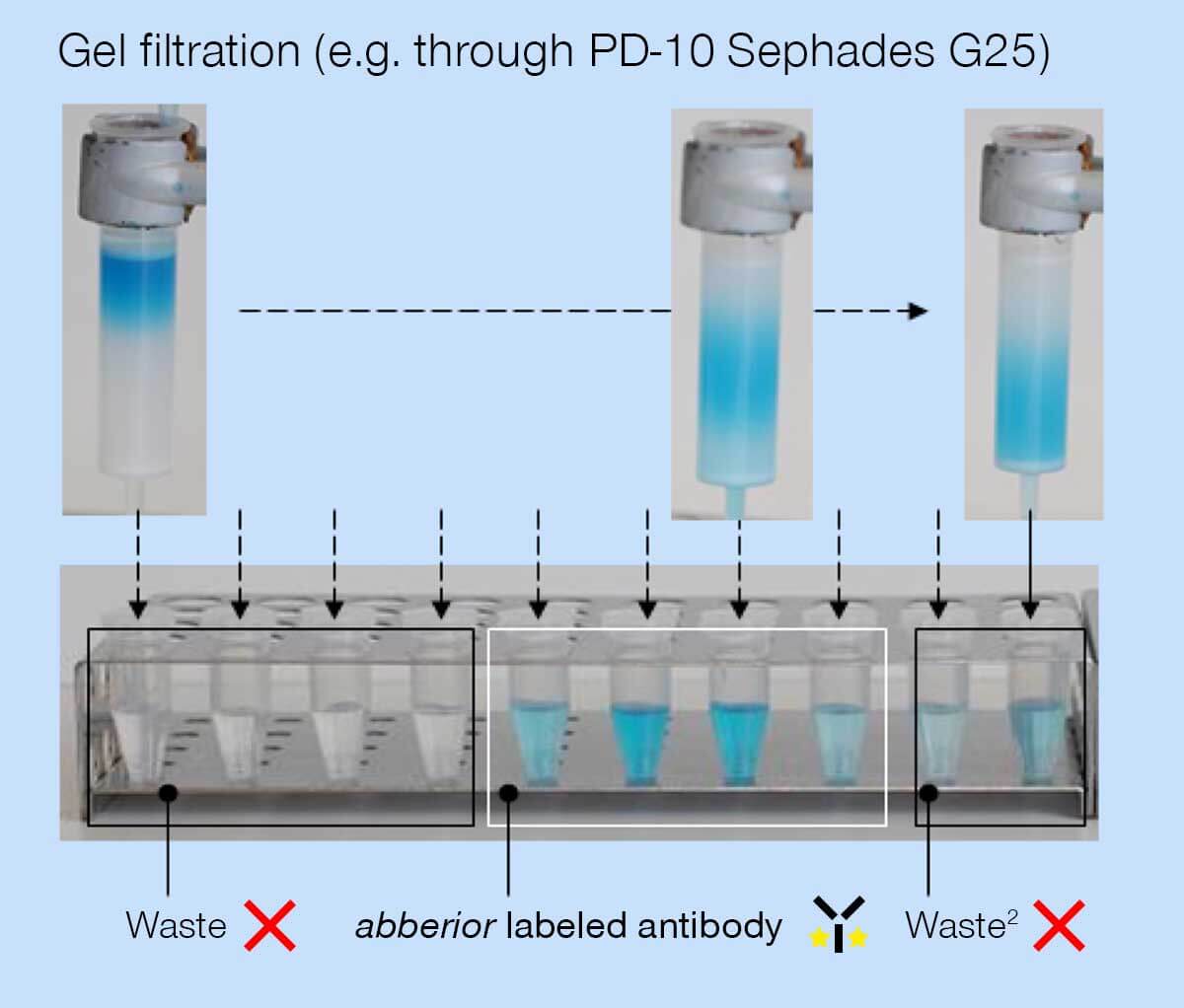
- Determine the protein concentration in each fraction (e.g. using a Bradford assay or a Nanodrop) and combine the fraction containing a sufficient protein concentration.
- Determine the protein concentration of the final solution (e.g. using a Bradford assay or a Nanodrop).
Optional: If the protein concentration is too low, the solution can be concentrated higher using appropriate protocols.
Optional: The average number of dye molecules per protein can be determined by the Degree of Labeling (DOL).
Optional: For a longer shelf life of the labeled antibody, BSA can be added as a stabilizer at a concentration of 2 mg/ml.
- Store the dye-labeled protein for a short time at 4 °C and for long-term storage at –20 °C to –80 °C.
Optional: To avoid freeze-thaw cycles split the protein solution into smaller aliquots.
Abbreviations
PBS Phosphate-buffered saline
BSA Bovine Serum Albumin
DMF N,N-Dimethylformamide
DMSO Dimethylsulfoxide
DOL Degree of Labeling
h hour